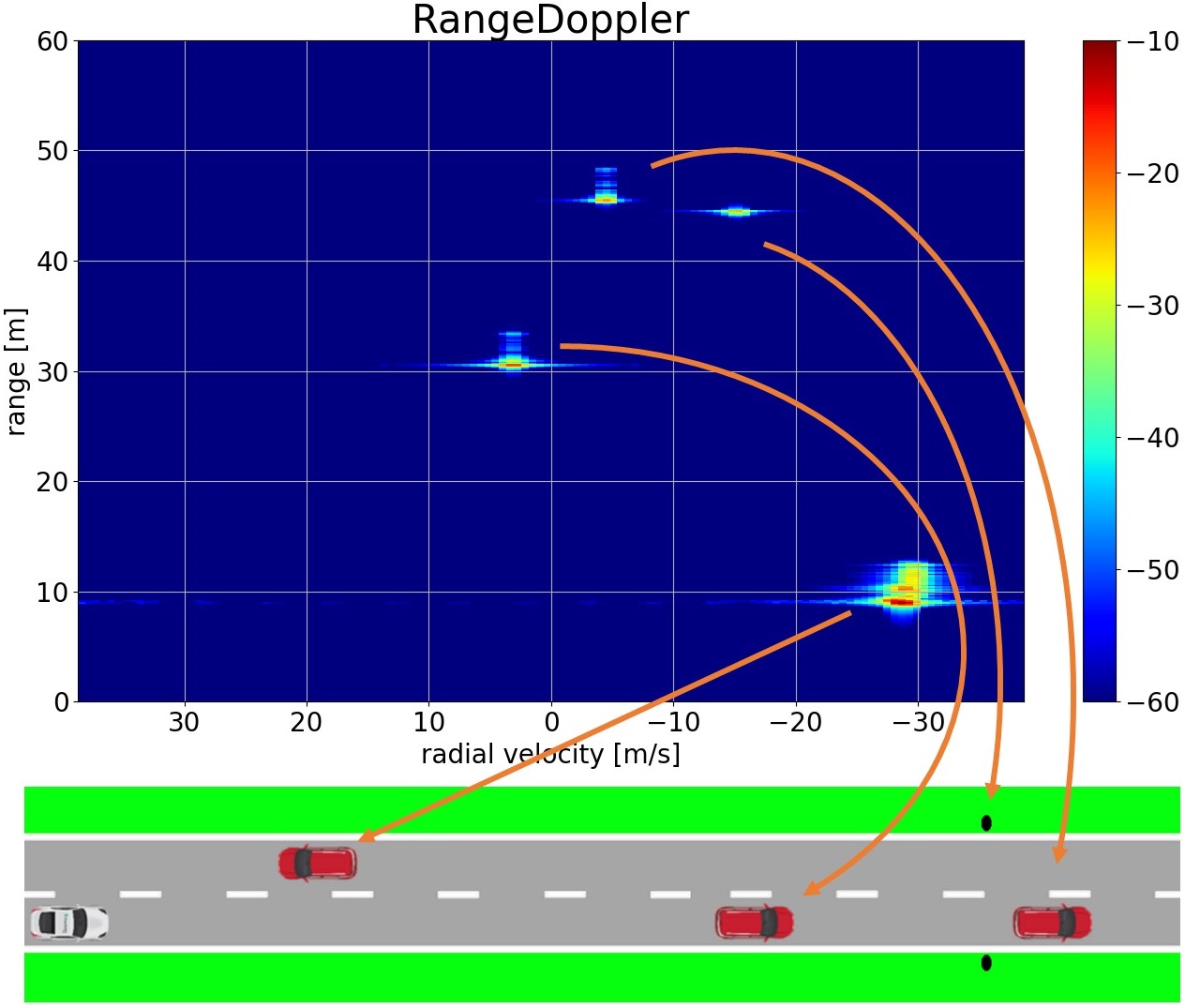
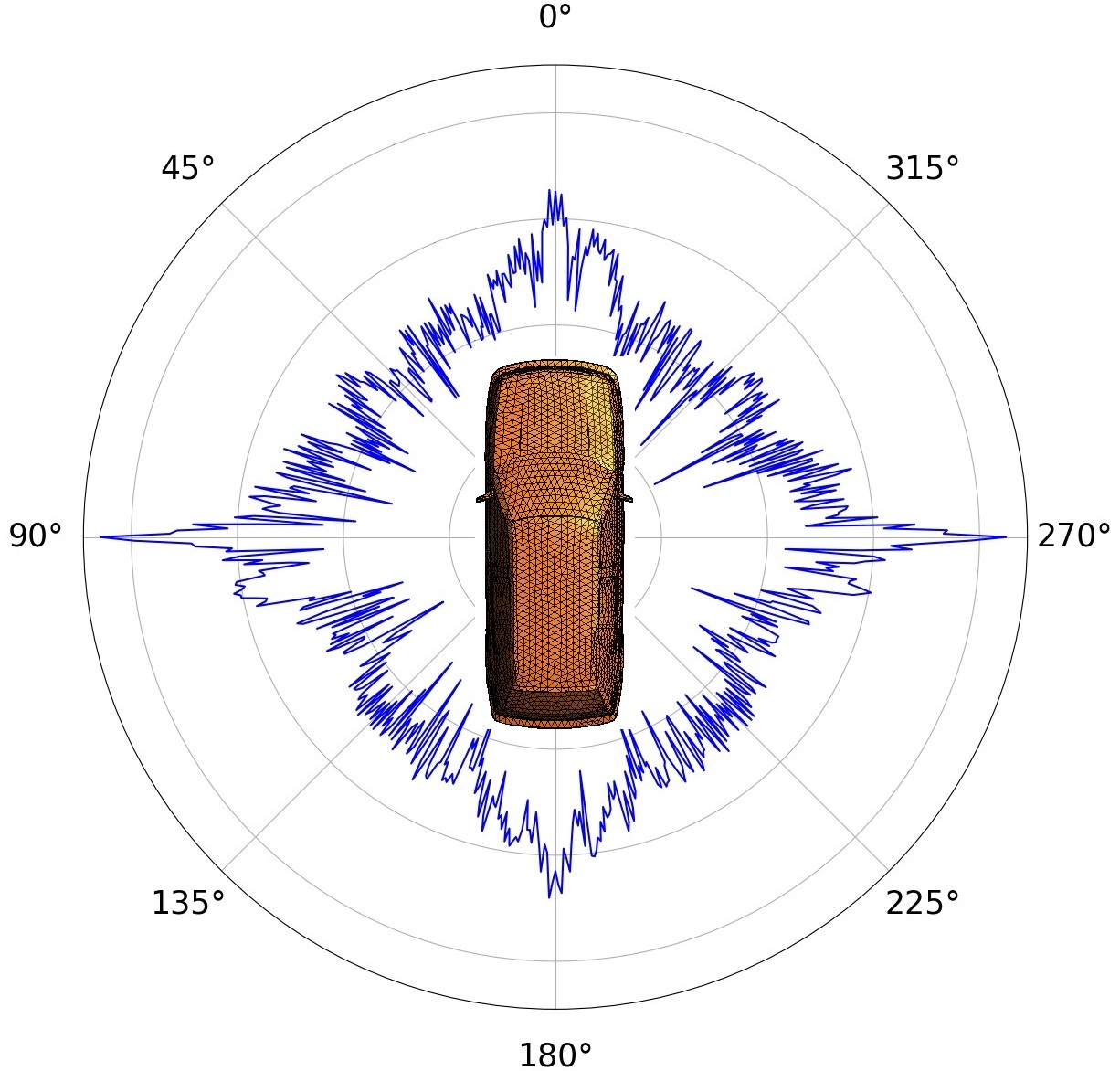
Automotive radar sensors are an essential component of existing driver assistance systems and play an important role for the future of autonomous driving. The reliable function of such radar sensors can be investigated with the help of hardware-in-the-loop or software-in-the-loop tests based on simulated data.
In order to determine the characteristics of radar signatures generated by road users, traffic scenarios must be modeled and analyzed electromagnetically. For this purpose, researchers at Fraunhofer FHR are developing the EM simulation software GOPOSim. This software makes it possible to simulate time-dynamic traffic scenarios electro-dynamically. In order to achieve efficient modeling and short simulation times, CAD models of the road users positioned in the corresponding traffic scene are loaded and transferred to a suitable scattering center model during runtime. In this way, GOPOSim computes the radar signatures of the traffic scenarios in a time-discrete manner, taking into account the physical properties.
 Fraunhofer-Allianz Verkehr
Fraunhofer-Allianz Verkehr